
|
20 agosto 2024
Satellites can have different purposes, such as Earth observation, telecommunications, navigation or scientific research. Before launching a satellite, it must be designed and built according to the specific objectives demanded by the different mission clients. The design must take into account:
This process ends with a series of extremely exhasutive tests, which simulate the extreme conditions to which the satellite will be subjected in space throughout its more than 15 years of lifetime.
Once the satellite is designed and built, it is transported to the launch site. Launch vehicles are rockets specially designed to transport one or more satellite payloads to a specific orbit and release it at the appropriate location.
Orbit selection is a crucial factor that depends on the purpose of the satellite:
Before launch, multiple tests are carried out to ensure that everything is in order:
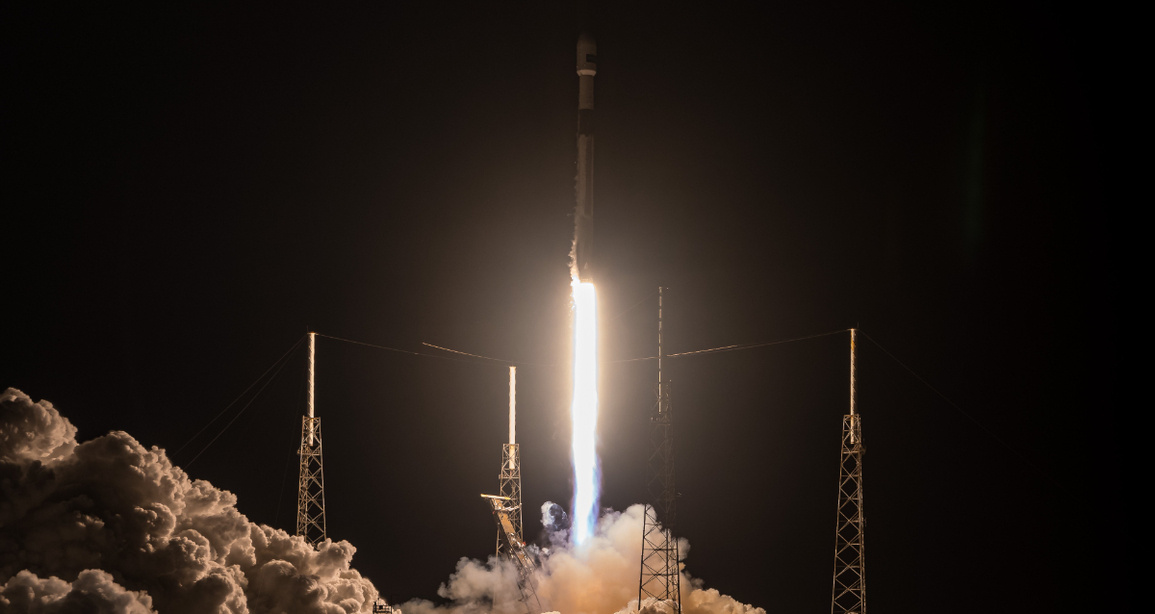
The launch is one of the most critical moments of the entire mission. It involves the ignition of the rocket's engines and its ascent through the atmosphere so that the satellite begins its journey to its orbital position. During this process, the trajectory and status of the rocket must be carefully monitored.
Once the rocket and satellite separate, the latter will deploy its solar panels, send the first telemetry signals and ignite the apogee engine, through which it will reach - in a journey that can last several months - a provisional orbit, where it will undergo new tests. After passing these, it will move to its final position and begin to provide services. Its status is controlled and monitored from Earth, making periodic adjustments to its orbit and systems if necessary.
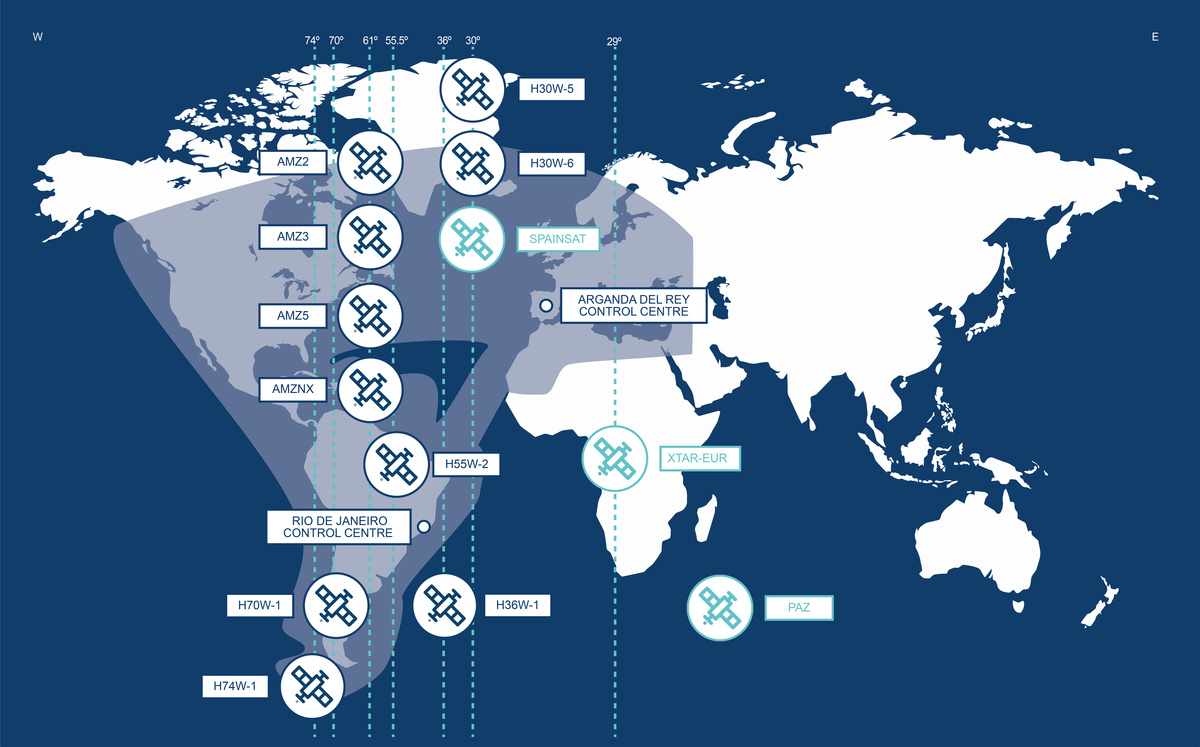
Currently, our company has 10 satellites in orbit, designed to provide connectivity services throughout the American continent, the Atlantic Ocean, Europe and North Africa. Thanks to them, we bring broadband solutions to the most remote areas of the planet, or even to airplanes and ships on the high seas. In addition, through our subsidiary Hisdesat, we offer government and defense services through three other satellites.
Below you can see our coverage map:

23 julio 2024
A cellular network, also known as a telephone network or mobile network, is a wireless communications infrastructure that enables the transmission of data and voice between mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices, via radio waves.

16 septiembre 2024
An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company or organization that provides individuals, businesses, or other organizations with Internet access through a variety of technologies such as broadband, DSL, cable, fiber optic, satellite, and wireless connections.