The low levels of connectivity in this sector are usually the result of the geographical location of the farms, in which the terrestrial infrastructure is not sufficiently deployed, and other conditions such as the limited information available in this regard.
Rural, unpopulated or difficult terrain areas are affected by poor coverage of terrestrial telecommunications infrastructure, preventing them from joining the digital transformation process. Specifically, in Spain around 3.2 million people still cannot access a quality network. This problem is more pressing in lands dedicated to crops or livestock, where the deployment of networks is more deficient than in large population centers, and represents an even greater difficulty in regions such as Latin America, where terrestrial infrastructures do not They have a deployment as wide as in Spain and in which the areas dedicated to the agricultural sector are much larger. This lack of connectivity prevents the application of digital processes for farm management in these areas.
Satellite technology has shown that it can be a very capable means of facing this challenge, allowing for Internet connection from any point, which makes it the ideal technological solution for the agri-food sector.
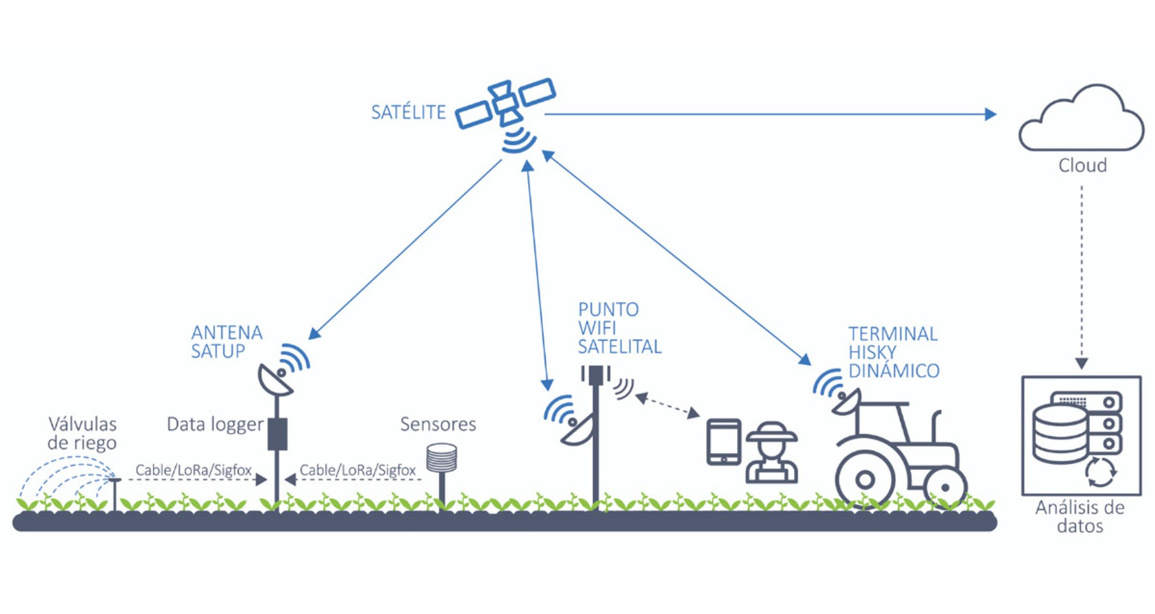
With a satellite terminal of small dimensions, low consumption and easy installation, it can be responsible for continuously transmitting the data sent from the sensors that monitor livestock or plantations. Also, self-pointing satellite terminals are an optimal solution to provide connectivity in mobility environments such as agricultural machinery. All of these terminals use solar energy, which allows them to expand their market share and reach territories that lack land communications, such as the agricultural entrepreneurs themselves, for whom it facilitates decision-making, increases their productivity and reduces consumption. of water, fertilizers and phytosanitary products. This technology also guarantees the traceability of products and contributes to minimizing the impact of agricultural activity on the environment.
According to the forecasts of the FAO 'Population Prospects 2019' report, the agri-food sector should be 70%-80% digitalized in the next 5 years to respond to the challenges that arise in this area. To make this objective possible, IoT (Internet of Things) solutions must be implemented that meet the specific demands of the agri-food sector, making the arrival of the so-called 'Agriculture 4.0' possible. That is, the digitalization, automation and streamlining of processes that boost the competitiveness of the sector thanks to greater precision in the use of resources: intelligent use of fertilizers, reduction of water consumption, monitoring of crops, control of diseases and pests, etc
At HISPASAT we have a portfolio of solutions for the agricultural world that includes robust, efficient and adaptable connectivity applications to the specific needs of each end client to facilitate their digital transformation, including services for IoT data transmission, device connectivity thanks to to a satellite WiFi network and data transmission of mobile agricultural machinery. These solutions are combinable with each other and independent of electrical and terrestrial telecommunications infrastructures. The universal coverage of its fleet over Europe, America and North Africa and the rapid deployment of user terminals make our satellites an ideal connectivity solution for an industry such as agri-food.
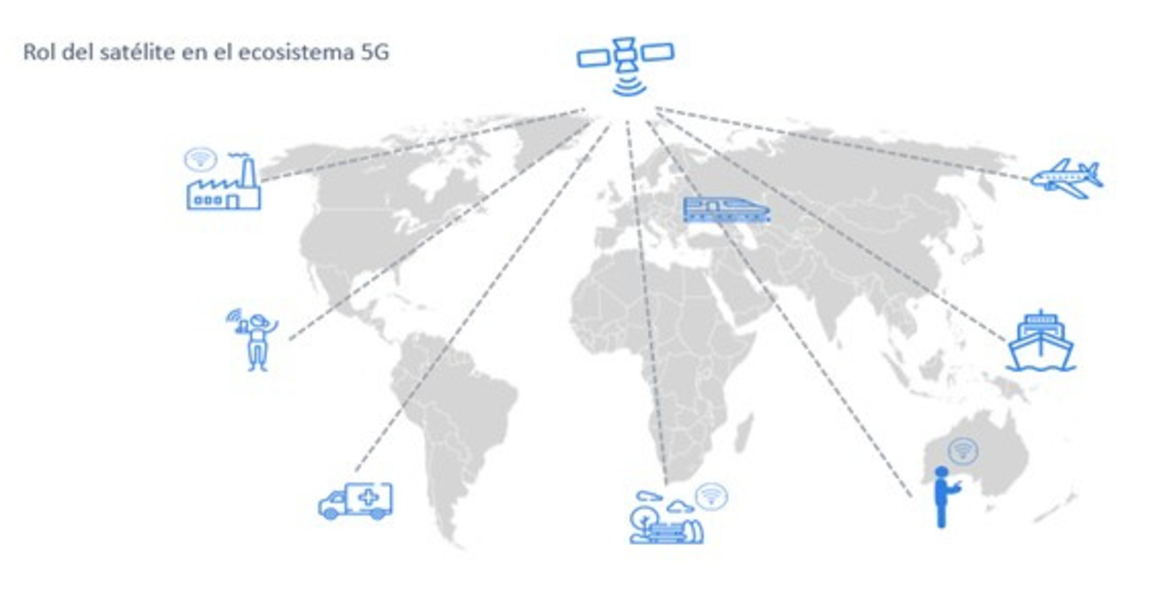
5G has been defined from its origin as a network of networks, the result of the confluence of different technologies towards a convergent scenario. If previous generations (2G, 3G, 4G) focused on connecting people, 5G aims to connect objects and people at all times wherever they are, both with other people and with other objects.

At HISPASAT we already knew the fundamental role that communications infrastructures have and this year 2020 has confirmed the importance that feeling connected at all times has acquired in our lives. That is why our team has given its best to work during such a complex year, where houses have become offices and we have had it more difficult than ever to be able to reconcile our workload with our other obligations; especially our controllers, who have made a 100% effort to offer a trouble-free service in times of such uncertainty.

The use of satellite allows hikers or workers to use wearable devices in remote areas to monitor their activity, detect falls or send alerts in the event of an accident so that emergency teams can act as quickly as possible.

Two years later, we return to the Mobile World Congress with a wide range of new developments in the field of satellite connectivity for remote and mobile environments that you can discover at our stand 7C50, located in hall 7.

We joined Fundación Repsol to provide satellite solutions to the largest project of this type in Spain.