
|
13 mayo 2024
Topologies are classified as either a physical network topology, which is the transmission medium for physical signals, or a logical network topology, which refers to the way data travels across the network between devices, regardless of the physical connection of the devices.
Examples of logical network topologies include “twisted-pair Ethernet,” which is classified as a “logical bus” topology, and “token ring,” which is classified as a “logical ring” topology.
Examples of physical network topologies include star, mesh, tree, ring, point-to-point, circular, hybrid, and bus topologies, each consisting of different configurations of nodes and links. The ideal network topology depends on the size, scale, goals, and budget of each company. A network topology diagram helps visualize communicating devices, which are modeled as nodes, and the connections between devices, which are modeled as links between nodes.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, each device is connected to another device through a specific channel. In a mesh topology, the protocols used are AHCP (Ad Hoc Configuration Protocol), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), etc.
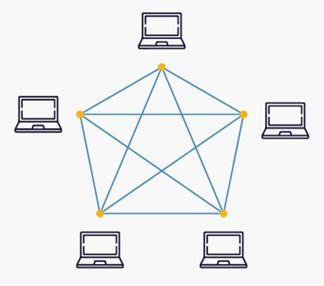
Advantages of Mesh Topology
Star Topology
In a star topology, all devices are connected to a single hub via a cable. This hub is the central node, and all other nodes are connected to the central node. The hub can be passive, meaning it is not an intelligent hub like broadcast devices, or it can be an intelligent hub, known as an active hub. Active hubs have repeaters. Coaxial cables or RJ-45 cables are used to connect computers. In a star topology, many popular Ethernet LAN protocols are used, such as CD (collision detection), CSMA (carrier sense multiple access), and so on.
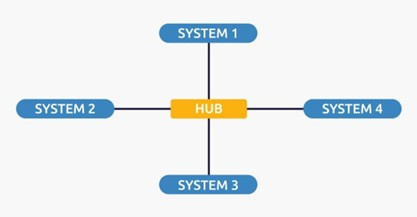
Advantages of Star Topology
Bus Topology
Bus topology is a type of network in which each computer and network device is connected to a single cable. It is bidirectional. It is a multipoint connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone fails, the topology fails. In bus topology, various MAC (Media Access Control) protocols are followed by Ethernet LAN connections, such as TDMA, Pure Aloha, CDMA, Slotted Aloha, etc.
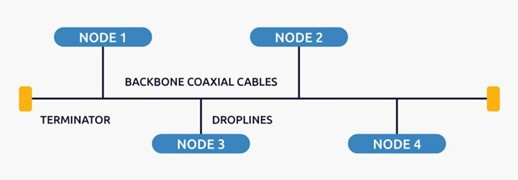
Advantages of this Topology
If N devices are connected to each other in a bus topology, then the number of cables required to connect them is 1, known as the trunk cable, and N drop lines are required.
Coaxial or twisted-pair cables are primarily used in bus-based networks that support speeds of up to 10 Mbps.
The cost of the cable is lower compared to other topologies, but it is used to build small networks.
The bus topology is a familiar technology, as the installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known.
Ring Topology
In this topology, a ring is formed that connects devices with exactly two neighboring devices.
Multiple repeaters are used for a ring topology with a large number of nodes because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in a ring topology with 100 nodes, the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Therefore, to prevent data loss, repeaters are used in the network.
Data flows in only one direction, i.e., unidirectionally, but it can be made bidirectional by having two connections between each network node. This is called a Double Ring Topology. In a ring topology, workstations use the Token Ring Passing protocol to transmit data.
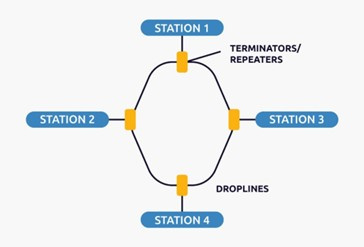
The most common access method in a ring topology is token passing.
Token passing: This is a network access method in which a token is passed from one node to another.
Token: This is a frame that circulates through the network.
The following operations that take place in a ring topology are:
Advantages of this topology
Tree Topology
This topology is a variation of the star topology. This topology has a hierarchical data flow. Tree topologies use protocols such as DHCP and SAC (Standard Automatic Configuration).
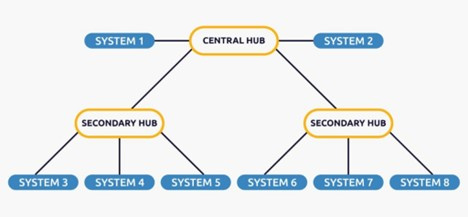
In this topology, the various secondary hubs are connected to the central hub containing the repeater. This data flows from top to bottom, i.e., from the central hub to the secondary hub and then to the devices, or from bottom to top, i.e., from the devices to the secondary hub and then back to the central hub. It is a multipoint connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone fails, the topology fails.
Advantages of this topology
Hybrid Topology
This topology technology is the combination of all the different types of topologies we studied previously. It is used when the nodes are free to take any shape. This means they can be individual topologies, such as ring or star, or they can be a combination of several of the topology types discussed above. Each individual topology uses the protocol discussed above.
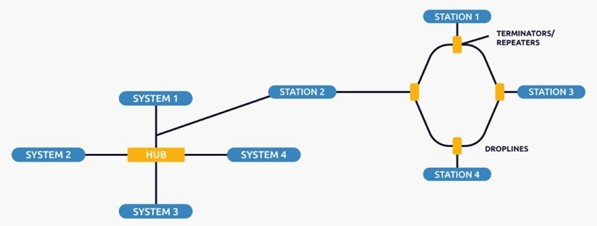
This topology is a combination of all the different types of networks.
Advantages of this topology
What is the importance of network topology?
A network's design has a direct impact on network functionality. Selecting the correct topology can improve data throughput and efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and reduce operating costs. Software-created network topology diagrams are important references for diagnosing network connectivity issues, investigating network slowdowns, and generally troubleshooting problems. One of the primary uses of network topology is to define the configuration of various telecommunications networks, including computer networks, command and control radio networks, and industrial fieldbuses.
We offer an intelligent network management solution (MNGM), which will facilitate corporate network management.

01 abril 2024
This new scalable, hybrid product optimizes user experience by combining the best of the GEO and LEO orbits and simplifying operations with an efficient, centralized management.

11 julio 2024
This new solution enables a permanent montiroization of these points thanks to the information provided through sensors and uploaded to a cloud platform that can be integrated with other customer management tools.